Multidimensional Sleep Health Definitions and Implications for Cardiometabolic Health
Published: April 14, 2025
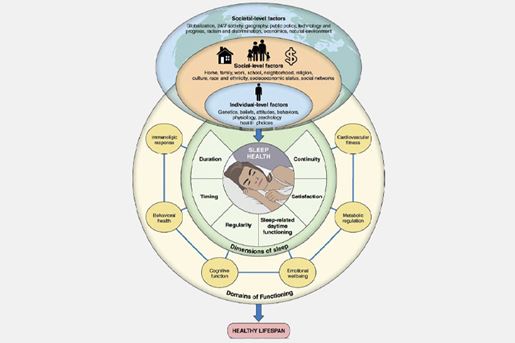
- Sleep health is associated with heart disease and stroke, cardiovascular mortality, and related cardiometabolic risk factors including blood pressure, lipids, inflammation, obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet. This evidence led to the inclusion of sleep duration as an eighth metric of overall cardiovascular health in the American Heart Association’s Life’s Essential 8.
- Sleep health is a positive, multi-faceted model that goes beyond the absence of known sleep disorders or short sleep duration. Common sleep dimensions included as components of multidimensional sleep health include regularity/rhythmicity, satisfaction/quality, alertness/sleepiness, timing, efficiency, duration, disturbed sleep, and sleep architecture.
- More research is needed using standardized measurements and definitions, along with studies showing how various combinations of sleep dimensions may increase cardiovascular risks. There is also a need for causal and mechanistic evidence that improving sleep health leads to better cardiometabolic health, to guide public health recommendations.
Video: Multidimensional Sleep Health
Writing Group Chair Marie-Pierre St-Onge, PhD and Vice Chair Michael A. Grandner, PhD announce the publication of a new scientific statement on sleep health and review some of new concepts informing the science presented in the paper.
Recommended Reading
- Impact of Sleep Disorders and Disturbed Sleep on Brain Health
- Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct of Cardiovascular Health
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease
- Sleep Duration and Quality: Impact on Lifestyle Behaviors and Cardiometabolic Health