Hypertension and the Gut Microbiome
Published: July 17, 2025
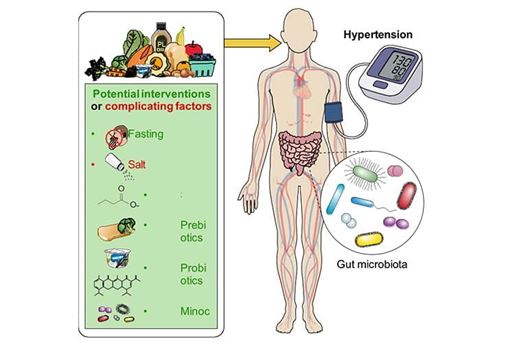
- Recent advances in gut microbiome and hypertension research suggest a novel therapeutic opportunity: targeting the gut microbiome to control blood pressure.
- Short chain fatty acids (e.g. acetate, propionate, butyrate) attenuate blood pressure in rodent models. In humans, prebiotic supplements that increase short-chain fatty acid production appear to reduce blood pressure, whereas direct oral butyrate supplementation may raise it.
- Fecal microbiome transplantation temporarily lowers blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Supplementation with prebiotics may enhance the blood pressure-lowering effect. Further research is needed to determine how these and other microbiome-targeted therapies can be effectively translated into clinical practice.