Pharmacological Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in the Fetal and Neonatal Periods
Published: February 05, 2024
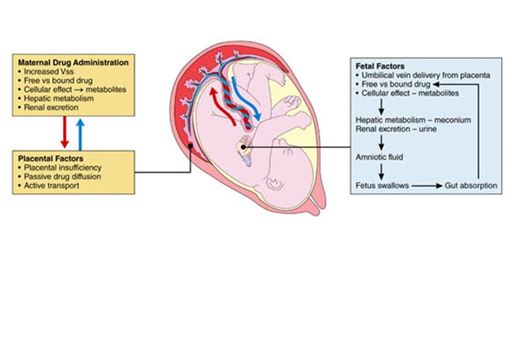
- Fetal and neonatal arrhythmias occur in approximately 1 per 4,000 live births and are an important cause of morbidity and mortality, with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial flutter (AFL) being the most common significant arrhythmias.
- Fetal arrhythmias can be treated with antiarrhythmic drug therapy to restore normal fetal heart rate, prevent/reverse fetal heart failure, and avoid premature delivery and its consequences.
- While there are no established strategies or algorithms for management of these diverse arrhythmias, the goal is to identify best practices for antiarrhythmic treatments and to limit unnecessary and potentially toxic drug exposure in the fetus, neonate, and pregnant patient.